There are 10 facts about bone density tests that will amaze you. For example, do you know that the results of bone density tests are expressed as T-scores and Z-scores? T-scores are used to diagnose osteoporosis, while Z-scores are used to diagnose osteopenia.
The National Resource Center on Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is the nation’s leading source of information on osteoporosis and bone health. They provide patient education, medical education, and human services to help people prevent, diagnose, and treat osteoporosis and related bone diseases.
Bone Density Tests
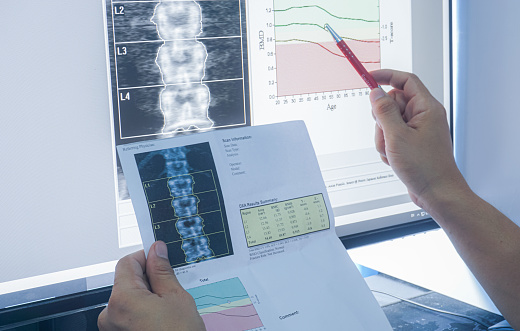
Bone density tests are used to measure bone density or the amount of bone mineral content in a particular area. Bone density is a key factor in determining bone strength and the likelihood of developing osteoporosis or other bone diseases. The term “bone density test” may refer to two different types of exams: a Bone Density Scan or a Bone Mineral Density (BMD) test. Bone density tests are typically performed using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT). The results of bone density tests are reported as a T-score, which compares the test subject’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult. A T-score is a comparison of your bone density to that of a young adult with peak bone mass. A T-score of -1 or above is considered normal, while a T-score of -2.5 or below indicates low bone mass and an increased risk for fractures. Bone density tests are often used to detect osteoporosis, assess fracture risk, and monitor the effects of certain cancer treatments on bone health.
Bone density testing is a quick and easy way to determine if you are at risk for developing osteoporosis or other bone diseases. A bone density test measures your bone mineral content (BMC) and can be used to diagnose osteopenia (low bone mass) or osteoporosis (severely low bone mass).
There are several different types of bone density tests, but the most common is a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. A DXA scan is generally considered the gold standard for diagnosing osteoporosis. Additional categories of bone density tests involve quantitative ultrasound (QUS), quantitative computed tomography (QCT), and peripheral dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (pDXA).
How To Measure Bone Density?

Bone density tests are used to measure bone density, which is the number of bone minerals in bone tissue. The test is also called bone densitometry, bone mineral density testing, or bone mass measurement. Bone density tests are used to diagnose osteoporosis, which is a condition characterized by low bone mass and bone loss. Osteoporosis can lead to fractures, especially of the hip, lower spine, and wrist.
Bone density tests are also used to identify people who are at risk for osteoporosis and to monitor people who have the condition or are being treated for it. The test is painless and quick, usually taking less than 10 minutes. Bone density tests are not used to diagnose osteoporosis, but they can help predict your risk for broken bones in the future and avoid an increased risk of bone fractures. A bone density test uses two types of technology: peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT) and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA). DXA is the most common type of bone density test. It measures bone density at the hip and spine. pQCT measures bone density at the radius, which is one of the bones in the forearm. Bone density tests are performed in a healthcare provider’s office or a medical facility such as a hospital or imaging center. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends that all women aged 65 years and older should have a bone density test. If you are younger than age 65 and have certain risk factors for osteoporosis, such as a family history of the disease or low body weight, your doctor may also recommend a bone density test. Bone densitometry is often performed as part of a medical education process for patients at high risk for osteoporosis, such as those with a family history of the condition or those taking steroid medications. The NIH osteoporosis program at the center is world-renowned. They offer dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) to diagnose osteoporosis and calculate your risk for fractures. Bone densitometry may also be recommended for pregnant women or young adults who have sustained bone fractures. The Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research recommends it too.
10 Facts About Bone Density Tests
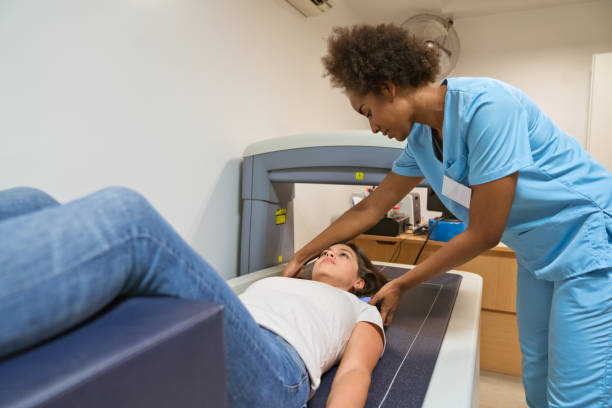
1. Bone density tests are used to diagnose osteoporosis, which is a disease that causes bones to become weak and break easily.
2. The test is also used to monitor the effects of osteoporosis treatments.
3. Bone density tests are safe and painless.
4. They are usually performed on the lower spine, hip, and forearm.
5. The test involves passing a scanner over the bones being tested.
6. The scanner measures the amount of calcium and other minerals in the bones.
7. A low bone density score indicates that you have osteoporosis or are at risk for developing it.
8. Osteoporosis can be prevented by getting enough calcium and vitamin D.
9. A bone density test does not require special preparation, although patients should avoid taking calcium supplements or antacids for 24 hours before the test.
10. Those with a family history of osteoporosis or related bone diseases are more likely to experience weakened bones and fractures.
Advantages Of Bone Density Testing?
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent future fractures and keep your bones healthy. A bone density test can also help to detect fractures that have already occurred.
Peak bone mass is the measure of the bones’ strength and density. It is determined by both heredity and lifestyle choices. There are several ways to measure peak bone mass. A DEXA scan is the most common method. This uses x-rays to measure bone mineral content and density. A quantitative computed tomography (QCT) scan or a bone scan can also be used to measure density. T-scores are used to compare an individual’s bone density with that of a healthy young adult. A score of -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis. The risk for fracture increases as t-scores decline. Peak bone mass is important because it can help to prevent future fractures. Those with lower bone density are more likely to break bones, even with everyday activities such as walking or lifting objects. The rebuilding process also takes longer, so the bones may not be as strong as they were before the fracture occurred. Certain cancer treatments, compression fractures, and certain skin diseases can also lead to lower bone density and increased fracture risk.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis is a disease that leads to the thinning of bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. It affects men and women of all ages but is most common in older adults. Osteoporosis can be caused by several factors, including family history, low calcium intake, lack of physical activity, and certain medications. The best way to prevent osteoporosis is to get enough calcium and vitamin D, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking. If you are at high risk for the disease, your doctor may also recommend bone density tests and other medical interventions.



