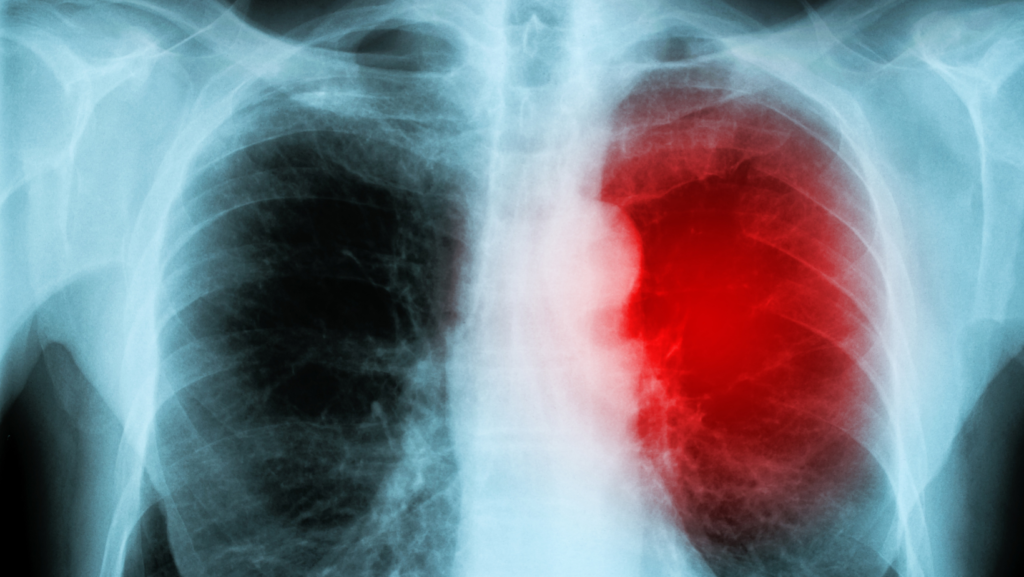
Myocarditis is a condition that causes inflammation of the myocardium, which is the muscular layer of the heart. The myocardium contracts and relaxes to pump blood throughout the body. Myocarditis can cause a wide variety of symptoms, depending on its severity. It can also be difficult to diagnose, as many of its symptoms are similar to those of other conditions.
In this article, we will discuss the symptoms and treatments of myocarditis. We will also provide some information on how to prevent this condition.
There are two types of myocarditis: acute and chronic. Acute myocarditis is a sudden, short-term inflammation of the myocardium. It is often caused by a viral infection, such as the flu or the common cold. Chronic myocarditis is long-term inflammation of the myocardium. It is often caused by autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
There are many different causes of myocarditis. It can be caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection. It can also be caused by an autoimmune reaction, in which the body’s immune system attacks the myocardium. Myocarditis can also be caused by certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs.
Myocarditis symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, the most common symptom is chest pain. This pain can be sharp or dull and may worsen with activity. Other symptoms of myocarditis include:
Myocarditis is typically diagnosed using a combination of tests. These tests may include:
A physical examination may also be used to diagnose myocarditis. The doctor will check for signs of inflammation, such as a swollen liver or fluid accumulation in the lungs. They will also listen to the heart and lungs with a stethoscope to look for abnormal sounds.
Blood tests can be used to look for signs of inflammation, such as an elevated white blood cell count. They can also be used to check for evidence of a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection.
Imaging tests, such as an echocardiogram, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, can be used to assess the damage to the myocardium.
In some cases, a small sample of tissue from the heart may be removed and analyzed in order to confirm the diagnosis of myocarditis.
A chest X-ray may also be used to diagnose myocarditis. This test can show evidence of fluid accumulation in the lungs, which is a common symptom of this condition.
The treatment options for myocarditis will depend on the underlying cause. If the condition is caused by a viral infection, it may resolve on its own without treatment. However, if the condition is caused by a bacterial or fungal infection, antibiotics or antifungal medications may be necessary. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary so that the heart can be monitored and supported with medication.
If the condition is caused by an autoimmune reaction, immunosuppressive medications may be necessary to control the immune system. In some cases, a heart transplant may be necessary.
Myocarditis can lead to a number of complications, including:
Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms that can cause problems with the heart’s ability to pump blood. Arrhythmias can be mild or severe and can require treatment. Some common arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation, cardiovascular disease, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia.
Treatment for arrhythmias may include medications such as beta-blockers or antiarrhythmic drugs, or surgery.
Cardiomyopathy is a condition that weakens and enlarges the heart muscle. Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure and arrhythmias. It is a serious condition that often requires treatment.
Treatment for cardiomyopathy may include medications, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or diuretics. You may also need to have an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placed. In some cases, a heart transplant may be necessary.
Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. Heart failure can be mild, moderate, or severe. Symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and feet.
Treatment for heart failure may include lifestyle changes, such as exercising and eating a healthy diet. You may also need to take medications, such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or beta-blockers. In severe cases, you may need to be hospitalized and receive treatment with IV fluids and other medications.
If myocarditis is caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection, the infection can spread to other parts of the body. This can be a serious complication that often requires treatment.
Treatment for an infection may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal medications. You may also need to be hospitalized and receive treatment with IV fluids and other medications.
Sudden cardiac death is a sudden, unexpected death caused by an arrhythmia. It can occur in people with myocarditis. Sudden cardiac death is a serious complication that often requires treatment.
Treatment for sudden cardiac death may include an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), which is a device that shocks the heart if an arrhythmia occurs. You may also need to take medications, such as beta-blockers or antiarrhythmic drugs. In some cases, a heart transplant may be necessary.
There is no sure way to prevent myocarditis. However, you can lower your risk by avoiding exposure to viruses and other infections. You should also avoid coming into contact with chemicals that can cause an autoimmune reaction. If you have myocarditis, it is important to follow your treatment plan and take all of your medications as prescribed. This will help to prevent complications and keep the condition under control.
The prognosis for myocarditis varies depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the individual. In some cases, myocarditis resolves on its own and does not cause any long-term problems. However, myocarditis can be a serious condition that can lead to complications, such as arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, sudden cardiac death, and infection. Treatment is often necessary to manage symptoms and prevent complications. With treatment, the prognosis is often good. However, myocarditis can be a life-threatening condition, and some people may not recover.
Myocarditis is a condition that causes inflammation of the heart muscle. It can be caused by viral infections, bacterial infections, autoimmune diseases, or exposure to chemicals. Myocarditis can be a serious condition that can lead to complications, such as arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, heart failure, sudden cardiac death, and infection. Treatment is often necessary to manage symptoms and prevent complications. With treatment, the prognosis is often good. However, myocarditis can be a life-threatening condition, and some people may not recover.