A bulging disc is a common injury that can occur in the neck or lower back. The discs are the soft, spongy tissues that separate the vertebrae and act as shock absorbers. A herniated disc also called a herniated lumbar disc, is when one of these discs pushes out from between the vertebrae. This can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the affected area.
Bulging discs are often diagnosed through a combination of symptoms, medical history, and imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury but may include medication, physical therapy, or surgery. In this article, we will discuss what a bulging disc is, how it’s diagnosed, and what treatment options are available.
A bulging disc is an injury to the discs that separate the vertebrae in your spine. These discs are made of a tough outer layer and a soft inner layer. The soft inner layer can sometimes herniate, or push out, through the outer layer. This can happen due to an injury or simply from aging and wear and tear on the discs.
When a disc herniates, it can press on the nerves around it. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area. A herniated disc most commonly occurs in the lower back, but it can also happen in the neck.
Bulging discs are different from herniated discs. A bulging disc does not herniate through the outer layer. Instead, the inner layer swells and pushes against the outer layer, causing the disc to bulge outwards. Although a bulging disc can be painful, it’s not as serious as a herniated disc.
A bulging disc is often diagnosed based on your symptoms and medical history. Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and when they started. They will also ask about your medical history, including any previous injuries or conditions that might be related to your current problem.
Your doctor will likely do a physical exam. This can help them rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms. They may also order imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to get a better look at the discs in your spine.
Treatment for a bulging disc depends on the severity of your symptoms and how well you respond to conservative treatments. Conservative treatments are those that do not involve surgery. These treatments can help relieve pain and improve function. They may include:
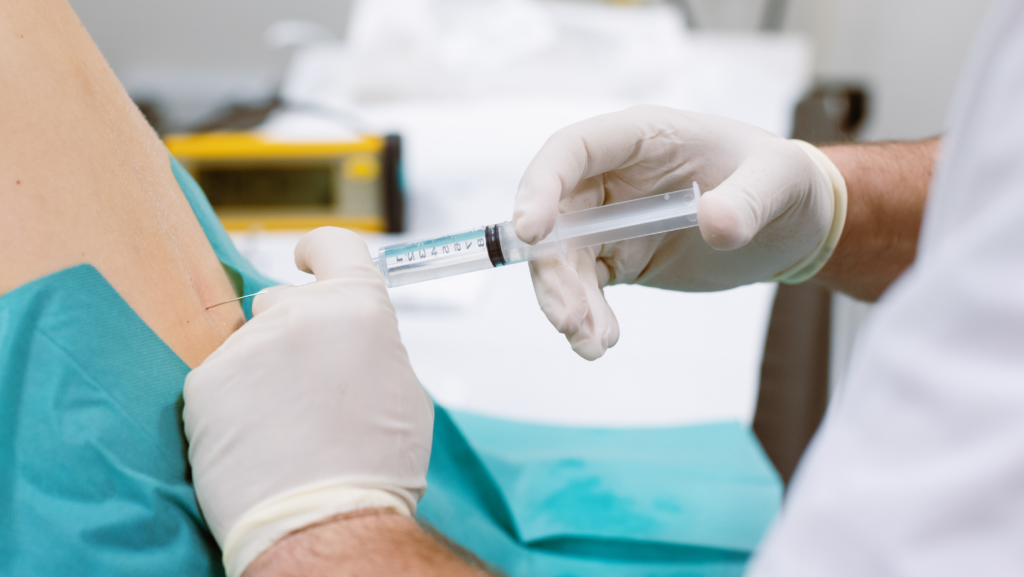
If conservative treatments do not help, your doctor may recommend injections. These can help relieve pain and improve function. Injections that are commonly used to treat a bulging disc include:
If you still have symptoms after trying conservative and injection therapies, surgery may be an option. Surgery is usually only recommended if you have severe pain or nerve damage. The type of surgery will depend on the location of the bulging disc and the severity of your symptoms. Surgery options include:
This is a procedure to remove the herniated portion of the herniated disk. It is often done using a microscope and small instruments.
This is a procedure to remove the lamina, which is the bony plate that covers the back of the spinal nerve canal. This pain medication procedure is often done to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve roots.
This is a procedure to fuse two or more vertebrae together. This can be done with metal implants and bone grafts. Spinal fusion can help stabilize the spine and relieve pain.
This is a newer procedure that involves removing the damaged disc and replacing it with an artificial disc. This surgery is less invasive than spinal fusions and may allow you to retain more mobility.
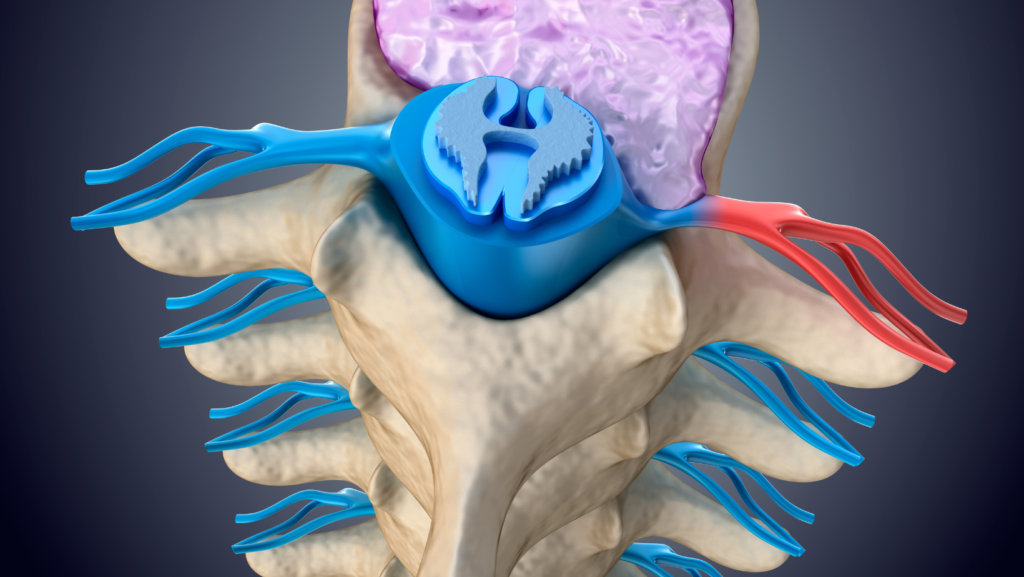
A bulging disc can sometimes cause complications. These can include:
The bulging disc can press on the nerves around it and cause damage. This can lead to pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area.
In severe cases, the bulging disc can compress the spinal canal cords. This can cause paralysis or loss of sensation in the affected area.
There are some things you can do to help prevent a bulging disc. These include:
Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight and keep your spine in good condition.
If you must lift a heavy object, use proper technique. Avoid bending at the waist. Instead, bend your knees and keep the object close to your body.
Stand up straight and avoid slouching. Use a chair that supports your back when sitting. When lifting something from the ground, squat down and lift with your legs, not your back.
Wearing high heels or shoes that are not supportive can put extra stress on your spine. Wear comfortable shoes with good arch support to help reduce strain on your lumbar spine.
Repetitive motions can put extra stress on your spine and increase your risk of developing a bulging disc. Try to vary your activities and take breaks often. If you must do the same activity over and over again, make sure to take frequent breaks.
Smoking increases your risk of developing a bulging disc. It also decreases blood flow to the discs, which can make them more likely to degenerate. If you smoke, quitting will help reduce your risk of developing a bulging disc.
If you have a family history of back problems or if you are concerned about your risk of developing a bulging disc, talk to your doctor. They can offer tips on how to prevent back problems and help you stay healthy. Thanks for reading! I hope this article was helpful in better understanding what a bulging disc is and how it’s treated.
A bulging disc is a common spine condition that can cause leg pain, numbness, and weakness. It is often treated with conservative measures such as rest, ice, and physical therapy. However, if these treatments do not relieve symptoms, injections or surgery may be necessary.
Complications from a bulging disc are rare but can include nerve damage and spinal cord compression. You can help prevent a bulging disc by maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding repetitive motions. If you are concerned about your risk of developing a bulging disc, talk to your doctor.