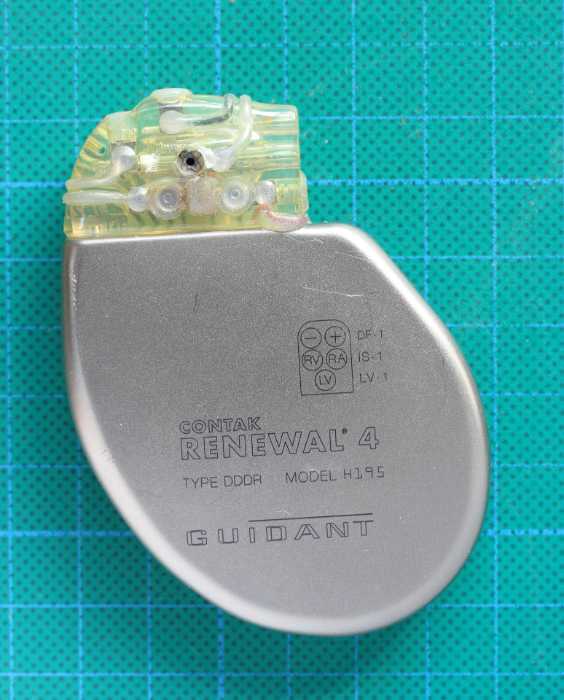
Pacemakers are devices that help control the heartbeat. They work by sending electrical impulses to the heart, which keep it beating at a regular rate. Pacemakers can be lifesavers for people with heart problems, and they have come a long way in terms of technology over the years. This blog post will take a closer look at how pacemakers work and some of the latest advancements in pacemaker technology!
What Are Pacemakers?
A pacemaker is a device that is implanted under the skin, usually on the chest. The pacemaker has two thin wires, called leads, connected to the heart. The component delivers electrical impulses through the leads to the heart muscle, which make the heartbeat.
Pacemakers are used to treat heart rhythm problems, specifically abnormally slow heartbeat. Magnetic resonance imaging helps improve heart rhythm which problems occur when the heart muscle contracts (squeezes) too slowly or irregularly. This can cause fatigue, shortness of breath, and dizziness. A pacemaker can help improve these symptoms by sending electrical impulses to the heart muscle to make it contract more regularly.
Pacemakers are also used to treat heart block. Heart block occurs when there is a delay or complete blockage of electrical signals between the upper and lower heart chambers. This can cause the heart to beat too slowly. A dual-chamber pacemaker can help improve this by sending electrical impulses to the heart’s lower chamber, which helps it contract more regularly.
How Do Pacemakers Work?
Pacemakers work by sending electrical impulses through the leads to the heart muscle, which make the heartbeat. The pacemaker uses a battery-operated generator to create these electrical impulses that are usually about the size of a half-dollar coin and are made of metal, plastic, and other materials that are safe for the body.
The artificial pacemaker has two leads: a positive lead and a negative lead. The positive lead has a small electrode at the end, placed in the heart’s right ventricle, and the negative lead has a larger electrode at the end, placed in the heart’s left ventricle.
The heart’s electrical system impulses travel from the generator, the leads, and the electrodes. The electrical impulses cause the muscles in the heart to contract and pump blood. The pacemaker can be programmed to send electrical impulses at different rates, depending on your needs. For example, if you have a heart block, your pacemaker may be programmed to send electrical impulses every few seconds or minutes.
Pacemakers are usually implanted under the skin on the chest, but they can also be implanted under the skin on the abdomen. The pacemaker is usually connected to the leads through a small incision in the skin.
After the pacemaker implanted in your heart is implanted, you will need regular checkups with your doctor to ensure it is working properly. You should also avoid strenuous activity and contact sports for six weeks after implantation to allow your incision to heal properly.
What Are The Latest Advancements In Pacemaker Technology?
The latest pacemaker technology advancements include smaller, leadless, and wireless pacemakers. Smaller pacemakers are less invasive and have a shorter recovery time. Leadless pacemakers do not have leads, meaning there is no need for an incision. Wireless pacemakers are pacemakers that are connected to the leads wirelessly.
What Are The Benefits of Pacemakers?

Pacemakers can improve symptoms of heart rhythm problems, such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and dizziness. They can also help treat heart block by sending electrical impulses to the heart’s lower chamber to make it contract more regularly. The latest advancements in pacemaker technology have made pacemakers smaller, less invasive, and have a shorter recovery time.
Who can Benefit from Pacemakers The Most?
People with heart rhythm problems or heart block can benefit from pacemakers the most. If you have a heart condition that is causing these problems, your doctor may recommend getting a pacemaker.
What Are The Risks of Pacemakers?
There are risks associated with pacemakers, such as infection, bleeding, and bruising at the implantation site. There is also a risk of lead dislodgement, which can occur when the lead moves from its original position. Lead dislodgement can cause heart rhythm problems.
It would help if you talked to your doctor about the risks and benefits of pacemakers before having one implanted.
How Much Do Pacemakers Cost?
The cost of pacemakers varies depending on the type of pacemaker you need. The average cost of a pacemaker is $5,000. Pacemakers can be implanted in hospitals, outpatient centers, and surgery centers. It would be best to talk to your doctor about where you can get yours implanted. Moreover, ensure you know the pacemaker cost and care options before the procedure is done.
What Is The Recovery Time For Pacemakers?
The recovery time for pacemakers is usually six weeks. You should avoid strenuous activity and contact sports during this time to allow your incision to heal properly. Additionally, you will need regular checkups with your doctor to ensure your pacemaker is working properly.
How Often Do Pacemakers Need To Be Replaced?
Pacemakers usually last about five to seven years. However, the battery life will depend on how often it is used. For example, suppose you have a pacemaker programmed to send electrical impulses every few seconds. In that case, the battery will need to be replaced more often than if you have a pacemaker programmed to send electrical impulses every few minutes.
FAQs
Can I have an MRI with a pacemaker?
Yes, you can have an MRI with a pacemaker. However, you should always consult your doctor before any procedures.
Can I go through airport security with a pacemaker?
Yes, you can go through airport security with a pacemaker. The TSA has special procedures in place for people with pacemakers. You can find more information on the TSA website.
What should I do if my pacemaker stops working?
If your pacemaker stops working, you should seek medical attention immediately. Your doctor will be able to determine if the problem is with the pacemaker or with your heart.
How do I know if I need a pacemaker?
Your doctor will likely recommend a pacemaker if you have heart rhythm problems or heart block. It would be best if you talked to your doctor about the risks and benefits of pacemakers before having one implanted.
Are There Any Alternatives to Pacemakers?
There are no alternatives to pacemakers. If you have an abnormal heart rhythm problem or heart block, your doctor may recommend getting a pacemaker. It is an ideal solution for most individuals suffering from heart problems.
Conclusion
Pacemakers are an important medical device that helps many people with heart conditions live long and healthy lives. Thanks to technological advances, pacemakers are constantly improving and helping more and more people. With the right pacemaker, you can live a long and healthy life! If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with a heart condition that requires a pacemaker, be sure to talk to your doctor about all of your options.
